Professional services firms are at an inflection point with a groundbreaking innovation: generative AI. This state-of-the-art technology, powered by sophisticated language models like GPT-3.5, holds immense promise for revolutionizing these firms’ operations, collaboration, and client service. Professional services firms deal with a wide range of unstructured data and content, including client communications, legal documents, qualitative analysis, client feedback, intellectual capital, and creative ideation. Understanding and leveraging this data is crucial for delivering expert advice, complying with regulations, and driving innovation in the professional services industry. Generative AI offers the potential to extract valuable insights and enhance decision-making from this wealth of unstructured data. However, as with any disruptive force, integrating generative AI into professional services workflows demands careful consideration.
While professional services firms may be keen to adopt generative AI, they must also navigate the challenges associated with security, sensitive data, and disruptions to mission-critical systems. In this blog post, we will explore the delicate balance between the remarkable opportunities presented to professional services firms by generative AI and the imperative of responsible implementation.
Weighing the Risk of Generative AI to Professional Services Firms
Professional services firms must exercise caution when implementing generative AI. When using APIs to access an engine like ChatGPT, there is the risk of sensitive data being passed into and out of the generative AI engines, like what happened in this recent incident. This is a critical point to address and considerations must be made for redacting and masking information in a manner such that it does not affect the effectiveness of the engine or create other business issues for professional services firms when dealing with sensitive client data.
Another risk to consider is the amplification of bias. Processes driven by core ERP systems require absolute accuracy and objectivity. The amplification of bias through AI could perpetuate incorrect assumptions and lead to disastrous outcomes. Therefore, if ERP systems incorporate AI components, it becomes essential to have robust maker-checker-approver layers before advancing to subsequent steps to mitigate potentially irreversible negative impacts on the business.
When seeking strategic advantages in both internal and external processes and developing specific use cases, it is crucial to carefully consider the trade-off between risk and reward. One commonly discussed concept is that of “centaur teams,” which consist of a combination of human and AI members. In these teams, AI assists humans in the development of new IT-led business services, while maintaining the vital principle that AI should augment human capabilities rather than take the lead.
What to Consider in Each Professional Services Business Area
Let’s look at the specific characteristics of the various professional services areas that differentiate the way Generative AI may be utilized.
Tax, Audit & Accounting (TAA)
Professional services firms rely on key financial principles and rules to prepare accurate financial statements, including balance sheets, income statements, and cash flows. However, interpreting accounting rules, such as transaction classification, often involves subjectivity. When utilizing generative AI to create reports or support financial statements, it is crucial to balance the speed of AI with appropriate checks and controls at each stage to prevent rework and missed deadlines.
Furthermore, accountants and auditors may seek specialized tools powered by generative AI, such as auto-generated macros, to streamline their daily tasks. In these cases, it is essential to develop standardized tools through focus groups comprised of stakeholders from across client engagements and services. This approach helps control complexity rather than allowing generative AI utilization to become an extreme form of citizen development.
Legal, Risk & Compliance (LRC)
Legal terminology often presents intricate complexities, making it an ideal use case for document generation through generative AI. Given the sensitivity and precision required in litigation arguments, utmost care must be taken to avoid legal liabilities arising from the improper disclosure of information or inaccurate communication leading to misrepresentation. While generative AI can assist in employing various logical reasoning strategies for legal arguments, human intuition checks remain essential to devise effective strategies.
People & Talent Management (PTM)
Automating administrative tasks typically carries minimal risk, but when it comes to communicating with individuals such as employees, recruitment candidates, the external public, and engaging on social media platforms, there is little room for error. Inaccurate or inappropriate communication in these contexts can potentially tarnish the organization’s reputation and therefore require strong human oversight. However, there is a strong case for the use of generative AI in the recruitment and hiring process. Given the increasing focus on diversity, equity, inclusion, and belonging (DEIB), it becomes crucial to eliminate any discernible biases. Generative AI can play a role in ensuring that hiring decisions are based solely on objective merit, while also taking into account employer policies and regulations to maintain compliance.
Advisory & Consulting (A&C)
Mergers and acquisitions require a high level of due diligence and a sharp eye for deal-breakers or factors that may cause failure after the transaction. Utilizing publicly available data can provide qualitative insights, and this is where generative AI can play a valuable role by conducting large-scale simulations to uncover potential vulnerabilities. However, caution must be exercised when incorporating synthetic data to supplement business data. It is essential to thoroughly evaluate both the qualitative and quantitative aspects of the industry and the entity before utilizing synthetic data to ensure accuracy and relevance.
Advertising & Marketing (A&M)
When evaluating the impact of generative AI on consumer experience, it may appear to be a less risky area for implementation compared to other operational aspects. AI-generated videos, images, audio and other content may appear to be an easy way for marketing teams to lessen the burden of heavy workloads. However, caution should still be exercised. AI-generated videos, although impressive, are often distinguishable from real ones, potentially leading to consumer dissatisfaction with their AI origin. In text-based campaigns like emails and social media posts, there is a risk of losing the contextual understanding of the consumer. Additionally, chatbots employed on websites or as social media auto-responders may struggle to detect sarcasm, even with improvements in algorithms. Conversely, marketing simulations, which primarily serve as decision-support tools in a secondary role, generally do not pose direct operational issues.
The exhibit below brings out some sample use cases in different categories (nature of the AI-assisted activity) for each professional services area, along with an approximate assessment of the complexity and volume of potential automation.
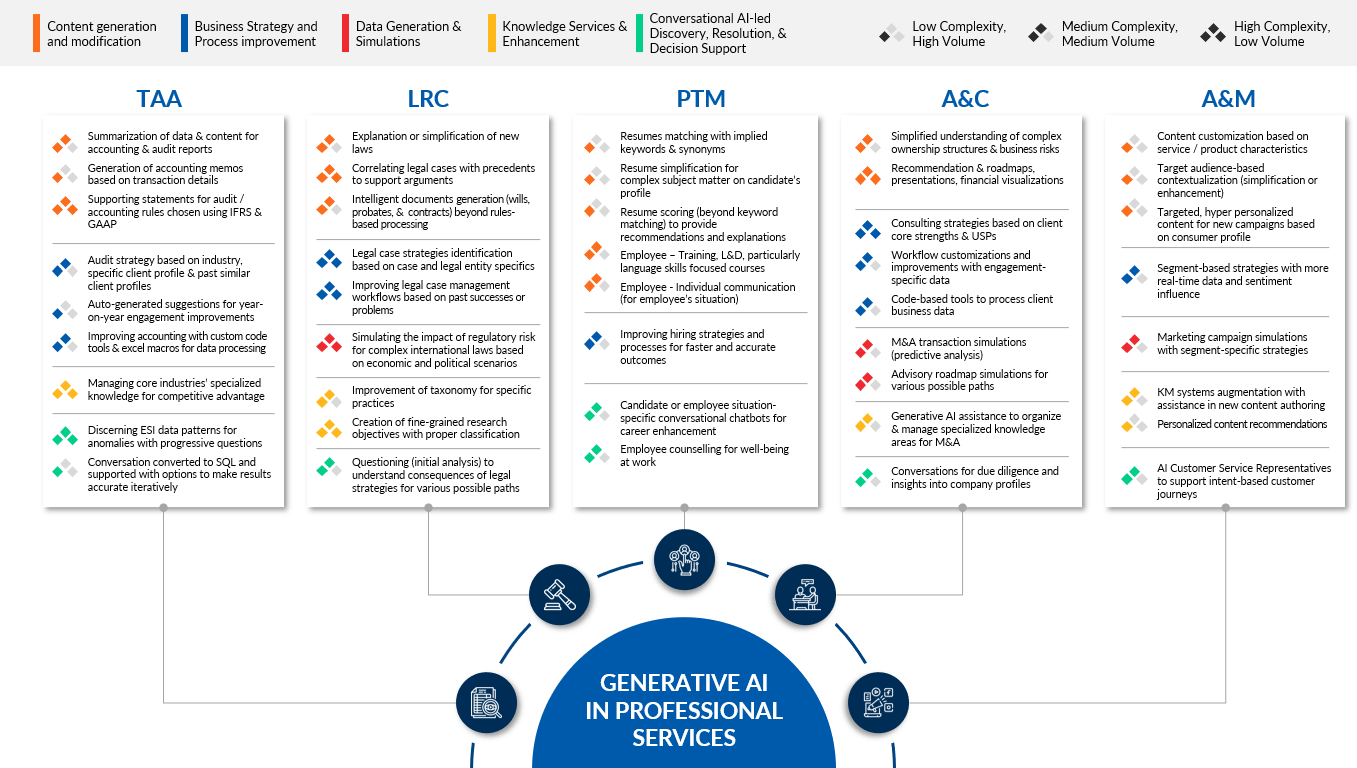
Key Strategies for Effective Generative AI Implementation Across Professional Services Business Areas
As the professional services sector heavily relies on expertise and judgment for decision-making, the integration of generative AI capabilities can serve as a valuable complement. It can support the verification of critical decisions, refine content, and, over time, facilitate the incorporation of changes to business models and processes following thorough scrutiny. To ensure effective implementation of generative AI, professional services firms should consider the following key strategies:
1. Establish Roadmaps with Strong Governance: Strategic thinking should be applied over a 3- to 5-year period to identify key performance indicators (KPIs) that can be transformed through generative AI, both internally and for specific clients. Qualitative assessments of risks introduced by generative AI should be conducted across various core and ancillary key result areas (KRAs), while minimizing potential negative impacts. These risks can be mapped to existing Enterprise Risk Management systems, allowing for independent tracking and composite risk ratings.
2. Adopt an Incremental Approach with Roll-back Support: For all business processes, low-risk implementations should be initially conducted as trials or proofs-of-concept (PoCs). As the impact of generative AI expands to other processes, the baselines of those processes should be incrementally strengthened. Generative models can be integrated as a separate layer to stabilize outputs and decisions, running parallel to core processes. As a process achieves high accuracy using generative AI, it can be marked as operationally sound. In case of any concerns or issues, fallback mechanisms can be initiated, reverting to the original processes for that specific area, following the principles of blue-green deployments commonly employed in modern DevOps practices.
3. Set Risk Limits: Taking inspiration from the concept of organizational risk appetite and extending it to organizational policy management, generative AI must be controlled within appropriate risk tolerance limits. Continuous and systematic feedback from various endpoints, including customers, system end-users, and field personnel, should be factored in. Monitoring systems can be implemented to raise alerts if generative AI-led responses are found to be inadequate, serving as inputs for continuous refinement and improvement.
By adopting these strategic considerations, professional services firms can effectively harness the potential of generative AI while managing associated risks and ensuring the delivery of high-quality services.
Conclusion
The transformative power of generative AI holds immense potential for revolutionizing various business areas within the professional services sector. However, implementing this technology requires a comprehensive evaluation of associated risks to core business processes. By adopting a phased approach that prioritizes low-risk processes, emphasizes incremental rollouts, establishes robust stabilization and rollback mechanisms, and incorporates ongoing risk monitoring and stakeholder feedback, professional services firms can truly harness the value of augmenting human expertise with AI.

















